Java多线程
Java多线程
线程简介#
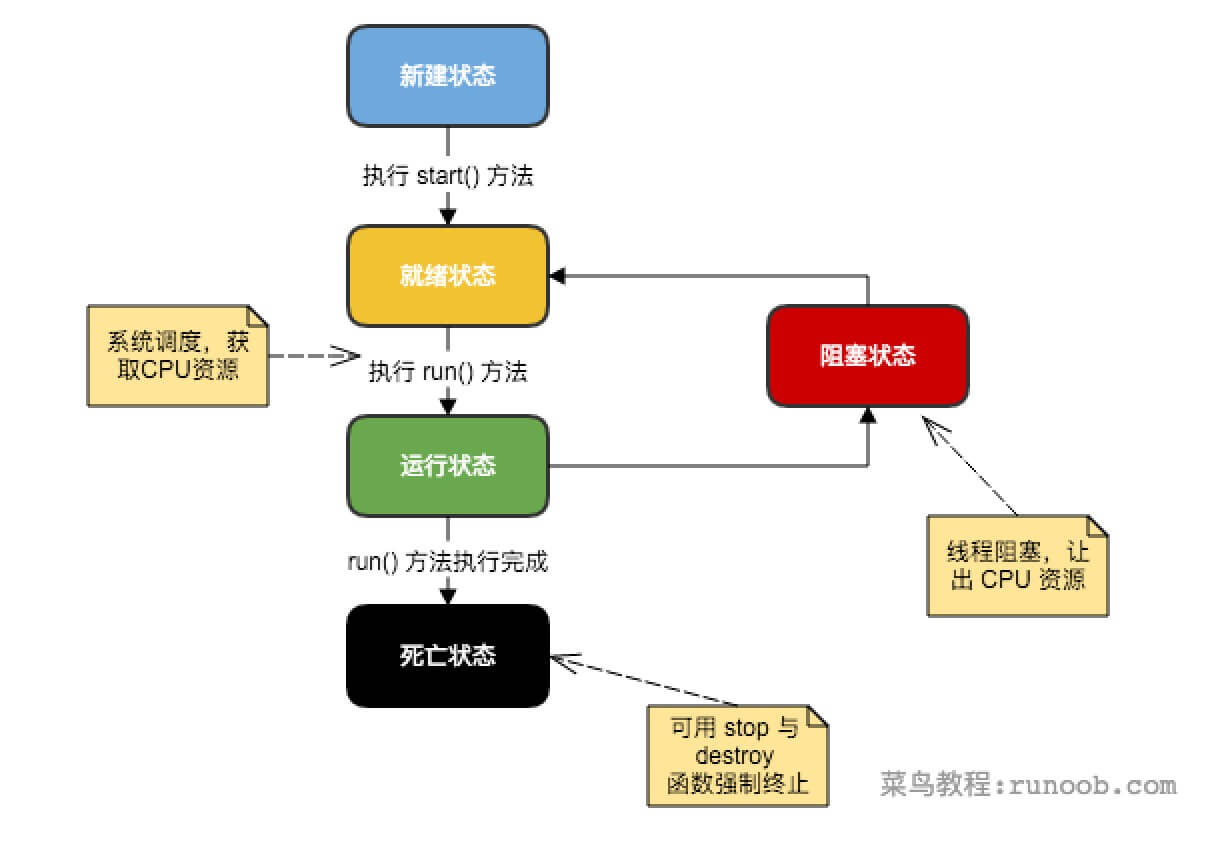
生命周期#
- 新建状态
- 就绪状态
- 运行状态
- 阻塞状态 / 等待阻塞 / 同步阻塞 / 其他阻塞
- 死亡状态
Java线程优先级#
Java 线程的优先级是一个整数,其取值范围是 1 (Thread.MIN_PRIORITY ) - 10 (Thread.MAX_PRIORITY )。默认情况下,每一个线程都会分配一个优先级 NORM_PRIORITY(5)。
线程相关接口/类介绍#
方法1、2:借助Runnable / Thread,无返回值#
interface Runnable { // thread task should be here public void run() {}}
class Thread implement Runnable { // thread constructor Thread(Runable[, String]) // override Runnable.run() @override public void run() {}
// get thread name, which is initialized at contructor public String getName() {}
// start thread/runnable run() task public void start() {}}根据上述关系,参考官方文档,要创建一个新线程任务:
- 创建一个实现Runnable接口的类,可以继承Thread,或者直接实现Runnable,重写run()方法,加入要完成的任务
- 传入Thread的构造函数,新建一个Thread实例
- 调用该Thread实例的start()方法
方法3:借助Callable / FutureTask,有返回值#
interface Callable<T> { public T call() {}}class FutureTask implement Runnable, Future, RunnableFuture { FutureTask(Callable<T>) {}
// return the task result of callable call()/ // Waits if necessary for the computation to complete, and then retrieves its result. public T get() {} // Waits if necessary for at most the given time for the computation to complete, and then retrieves its result, if available. public T get(long timeout, TimeUnit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException}根据上述关系,要创建一个有返回值的线程任务:
- 创建一个实现Callable接口的类,重写call()方法,加入要完成的任务,最后返回一个T类型的结果
- 传入FutureTask的构造函数,新建一个FutureTask实例
- 传入Thread的构造函数,新建一个Thread实例
- 调用该Thread实例的start()方法
- 在任务结束后调用FutureTask实例的get()方法(注意该方法是阻塞的),得到任务结果